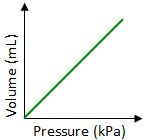
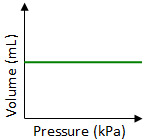

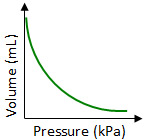
Which graph best shows the relationship between the volume of a gas and its pressure as the gas temperature remains constant?




A.
Incorrect. In Boyle’s Law the volume of a gas is inversely proportional to its pressure. In this graph, the volume and pressure are proportional to each other.
B.
Incorrect. In Boyle’s Law the volume of a gas is inversely proportional to its pressure. In this graph, the volume is not changing, but the pressure is.
C.
Incorrect. In Boyle’s Law the volume of a gas is inversely proportional to its pressure. In this graph, the volume and pressure either proportional to each other or the volume is remaining constant as the pressure changes.
D.
Correct! In Boyle’s Law the volume of a gas is inversely proportional to its pressure.
A gas has a volume of 100.0 mL at a pressure of 400.0 mm Hg. If the temperature is held constant, what is the volume of the gas at a pressure of 800.0 mm Hg?
A. 33.3 mL
Incorrect. In the calculation of P1V1 = P2V2,
the volume (V2) is equal to 50.0 mL.
B. 50.0 mL
Correct! In the calculation of P1V1 = P2V2,
the volume (V2) is equal to 50.0 mL.
C. 160.0 mL
Incorrect. In the calculation of P1V1 = P2V2,
the volume (V2) is equal to 50.0 mL.
D. 200.0 mL
Incorrect. In the calculation of P1V1 = P2V2,
the volume (V2) is equal to 50.0 mL.
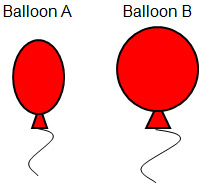
Each balloon has been filled with the same number of moles of helium gas. The balloons are both in a room with a constant temperature of 25.0 0C. Which of the following best explain why balloon B is larger than balloon A?
A. The gas in balloon A is under more pressure.
Correct! The gas in balloon A is under more pressure which is causing it to become smaller.
B. The gas in balloon B is under more pressure.
Incorrect. If the gas in balloon B was under more pressure, it would be compressed and be the smaller balloon.
C. The gas in balloon B is leaking out from its knot.
Incorrect. If the gas was escaping from the knot, balloon B would be smaller in size.
D. The gas in balloon A is changing into neon gas.
Incorrect. Helium gas cannot change into neon gas.
A 30.0 L sample of gas collected in the upper atmosphere at a pressure of 48.6 torr is compressed into a 1.50 L container at the same temperature. What is the new pressure?
A. 2.43 torr
Incorrect. In the calculation of P1V1 = P2V2,
the pressure (P2) is equal to 972 torr.
B. 972 torr
Correct! In the calculation of P1V1 = P2V2,
the pressure (P2) is equal to 972 torr.
C. 1.530 torr
Incorrect. In the calculation of P1V1 = P2V2,
the pressure (P2) is equal to 972 torr.
D. 2,190 torr
Incorrect. In the calculation of P1V1 = P2V2,
the pressure (P2) is equal to 972 torr.