Which of the following best describes the difference between chemical and physical changes?
A. Chemical changes always give off heat and light, and physical changes do not.
Incorrect. Chemical changes do not always give off heat and light.
B. Chemical changes result in a new substance being produced, and physical changes do not.
Correct!
C. Chemical changes are only a change in form, and physical changes result in a new substance.
Incorrect. Physical changes do not result in a new substance.
D. Chemical changes are reversible, and physical changes are not.
Incorrect. Physical changes and some chemical changes may be reversible.
Which of the following changes could be examples of physical changes of matter?
A. I and III
Incorrect. Water decomposing results in the formation of two new substances.
B. II and IV
Correct! Dissolving and crushing or grinding substances are examples of physical changes.
C. I and IV
Incorrect. The combustion of ethanol results in the formation of carbon dioxide and water.
D. I, II, and III
Incorrect. While choice II is an example of a physical change, choices I and III are examples of chemical changes.
Limestone is a sedimentary rock found in large quantities in central Texas. Which of the following best describes a chemical change to limestone?
A. Drilling into limestone deposits underground
Incorrect. Drilling is an example of a physical change.
B. Carving limestone into stones for buildings
Incorrect. Carving is an example of a physical change.
C. Limestone statues breaking down due to acid rain
Correct! The acid rain reacts with the limestone, which causes the statue to erode away.
D. Limestone deposits being washed away by a stream
Incorrect. Weathering of limestone is an example of a physical change.
|
Observations
|
|
A new substance is formed and has the properties described above. Which of these would be considered a chemical property?
A. II only
Incorrect. Color is a characteristic that describes a physical property.
B. II and III
Incorrect. Color is a characteristic that describes a physical property.
C. III only
Correct! The substance reacts with water to give off heat illustrating a chemical property of that substance.
D. I, II, and III
Incorrect. Color and volume are characteristics that describe physical properties.
A student recorded the following properties of a metal below in his notebook.
|
Observations
|
|
Which of these would be considered a physical property?
A. I only
Incorrect. Ductility and malleability are also physical properties of a substance.
B. II and III
Incorrect. The ability to react or combine with other substances is an indicator of substances chemical properties.
C. I and III
Correct! Melting point, ductility, and malleability illustrate substances physical properties.
D. II and IV
Incorrect. The ability to react or combine with other substances is an indicator of substances chemical properties.
A chemistry student’s investigation notes are outlined below.
|
Observations
|
|
The student decided that her unknown metal was magnesium. Which of the following is an extensive property of magnesium?
A. Strong, silvery-white metal
Incorrect. This choice represents an intensive property as it describes a property inherent to magnesium.
B. Mass of 0.79 grams
Correct! Extensive properties depend on the amount of matter present.
C. Produced a white light when ignited
Incorrect. This choice represents an intensive property as it describes a property inherent to magnesium.
D. Metal reacted with certain substances
Incorrect. This choice represents an intensive property as it describes a property inherent to magnesium.
Which of the following only includes extensive properties?
A. Volume, color, and malleability
Incorrect. Malleability is an example of an intensive property and does not depend on the amount of matter present.
B. Mass, volume, and density
Incorrect. Density is an example of an intensive property and does not depend on the amount of matter present.
C. Length, mass, and volume
Correct! These characteristics depend on the amount of matter present.
D. Conductivity, malleability, and density
Incorrect. These are all examples of intensive properties.
A chemistry student’s investigation notes are outlined below.
|
Observations
|
|
The student believes his unknown metal may be magnesium. Which of the following is an intensive property of magnesium?
A. It is an unknown substance.
Incorrect. Scientists use intensive properties to observe and identify unknown substances.
B. Silvery-white metal
Correct! The color of the metal is not dependent on the amount of matter present.
C. Mass of 0.93 grams
Incorrect. This is an example of an extensive property as it depends on the amount of matter present.
D. Length of 1.45 centimeters
Incorrect. This is an example of an extensive property as it depends on the amount of matter present.
Which of the following only includes intensive properties?
A. Volume, color, and malleability
Incorrect. Malleability is an example of an intensive property and does not depend on the amount of matter present.
B. Mass, volume, and density
Incorrect. Density is an example of an intensive property and does not depend on the amount of matter present.
C. Length, mass, and volume
Correct! These characteristics depend on the amount of matter present.
D. Conductivity, malleability, and density
Incorrect. These are all examples of intensive properties.
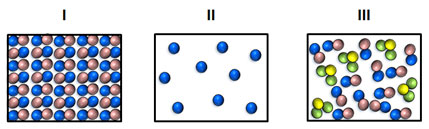
Which of the following depicts samples of matter in the gas phase only?

A. I only
Incorrect. Illustration I depicts an object in the solid phase.
B. I and II
Incorrect. Illustration I depicts an object in the solid phase.
C. III only
Incorrect. While illustration III could depict the gas phase, it is not the only choice that does so.
D. II and III
Correct! Illustrations II and III depict samples of matter in the gas phase.
Which of the following appropriately compares solids, liquids, and gases?
|
A. I and II
Incorrect. Solids are almost incompressible.
B. I and III
Incorrect. Solids have a fixed arrangement of particles.
C. II and IV
Correct! These choices appropriately compare the characteristics of solids, liquids, and gases.
D. I and III
Incorrect. Solids are almost incompressible.
Which of the following shows the states of matter in order of easiest to compress to hardest to compress?
A. Solid → Liquid → Gas
Incorrect. Solids are almost incompressible.
B. Liquids → Gas → Solid
Incorrect. Gases are more readily compressible than liquids.
C. Gas → Solid → Liquid
Incorrect. Liquids are more readily compressible than gases.
D. Gas → Liquid → Solid
Correct! Gas is the most compressible and solids are almost incompressible.
The following three items were poured into a container together:
|
Which of the following statements provides the correct classification of matter for each of the items above?
A. I only
Incorrect. Both calcium carbonate and copper chloride are pure substances.
B. I and II
Incorrect. Both calcium carbonate and copper chloride are pure substances; therefore, choice I is false.
C. III and IV
Incorrect. Iron, copper chloride, and calcium carbonate are pure substances.
D. IV only
Correct! All three items are pure substances.
Which of the following depicts a sample of a pure substance?
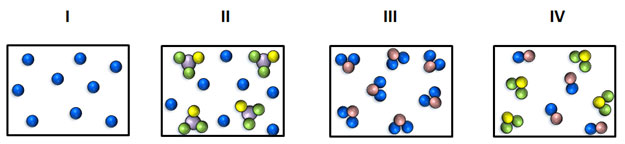
A. I only
Incorrect. Illustration I is not the only example of a pure substance.
B. IV only
Incorrect. Illustration IV is an example of a mixture.
C. II and IV
Incorrect. Illustrations II and IV are examples of mixtures.
D. I and III
Correct! Illustrations I and III correctly depict examples of pure substances.
Group II elements, such as magnesium (Mg), calcium (Ca), and strontium (Sr), have similar chemical properties because —
A. they have the same number of energy levels
Incorrect. Elements in the same period have the same number of energy levels.
B. they have the same number of valence electrons
Correct! Elements in the same group are similar because they have the same number of valence electrons.
C. they have the same number of neutrons
Incorrect. The number of neutrons does not determine an element’s chemical properties.
D. they have same number of protons
Incorrect. The valence electrons determine the chemical properties of an element.
Which of the following depicts a sample of a mixture?

A. II only
Incorrect. Illustration II is not the only example of a mixture.
B. I and III
Incorrect. Illustrations I and III are examples of pure substances.
C. III only
Incorrect. Illustration III is an example of a pure substance.
D. II and IV
Correct! Illustrations II and IV illustrate a mixture of two or more substances.
Halogens are highly reactive elements that react violently with metals, hydrogen, and water. If a chemical engineer needs to obtain two elements with similar chemical properties, they should use —
A. two elements from Group 2
Incorrect. Based on the answer choices, elements in Group 2 are not similar to the halogens.
B. two elements from Group 4
Incorrect. Based on the answer choices, elements in Group 4 are not similar to the halogens.
C. two elements from Group 17
Correct! The engineer would need to select two elements from Group 17, as they would be the most similar in chemical properties as these elements are in the same group as the halogens.
D. two elements from the transition metals
Incorrect. Based on the answer choices, transition metals are not similar to the halogens.
Which of the following best describes why elements in the same group of the periodic table have similar chemical and physical properties?
A. All elements in a group have the same number of protons.
Incorrect. Elements in the same group behave similarly because they have the same number of valence electrons.
B. All elements in a group have similar number of valence electrons.
Correct! Elements in the same group behave similarly because they have the same number of valence electrons.
C. All elements in a group have the same number of neutrons.
Incorrect. The number of neutrons does not determine the chemical properties of an element.
D. All elements in a group have the same atomic radius.
Incorrect. The number of atomic radius does not determine the chemical properties of elements in a group.
Dmitri Mendeleev, who is commonly referred to as the “father of the periodic table”, used the work of other scientists to arrange the elements according to atomic weight. His version of the periodic table differed from other scientists because he placed certain elements in new positions despite their atomic weights. Which of the following best explains why Mendeleev arranged these elements in order to group them with other elements?
A. Elements had similar physical changes
Incorrect. Mendeleev noticed patterns in the physical and chemical properties of elements and moved certain elements to new positions based on his observations despite their accepted atomic weights.
B. Elements had similar chemical properties
Correct! Mendeleev noticed that certain chemical properties were repeated periodically.
C. Elements had similar ability to form mixtures
Incorrect. The ability to form mixtures is not a chemical property of an element; nor did it help in sequencing elements on the periodic table.
D. Elements had similar ability to lose neutrons
Incorrect. Mendeleev noticed patterns in the physical and chemical properties of elements and moved certain elements to new positions based on his observations despite their accepted atomic weights.
The modern Periodic Table of Elements was arranged based on which of the following —
A. atomic mass
Incorrect. The periodic table was arranged based on atomic number.
B. atomic number
Correct! The modern periodic table was arranged by increasing atomic number.
C. isotopic mass
Incorrect. The periodic table was arranged based on atomic number.
D. oxidation number
Incorrect. The periodic table was arranged based on atomic number.
According to the general trends of the Periodic Table of Elements, which of the following elements has the largest atomic radius?
A. Sodium
Incorrect. Sodium is positioned further up on the periodic table and has a smaller atomic radius due to its smaller valence shell.
B. Cesium
Correct! Cesium has the largest number of valence shells and therefore a larger atomic radius.
C. Calcium
Incorrect. Calcium is positioned further up on the periodic table and has a smaller atomic radius due to its smaller valence shell.
D. Argon
Incorrect. Argon is positioned furthest to the right on the periodic table and has a smaller atomic radius due to its smaller valence shell.
Which of the following best explains why sulfur has a larger atomic radius than the oxygen atom?
A. The outer valence shell of sulfur is located farther away from the nucleus than that of oxygen’s outer valence shell.
Correct!
B. The outer valence shell of sulfur is located closer to the nucleus than that of oxygen’s’ outer valence shell.
Incorrect. Sulfur contains three energy levels. This would result in its valence shell being further out from the nucleus than oxygen.
C. Sulfur has more neutrons than oxygen and therefore it has a larger atomic mass.
Incorrect. This does not explain why sulfur has a larger atomic radius than oxygen.
D. Oxygen has more neutrons than sulfur and therefore it has a larger atomic mass.
Incorrect. This does not explain why sulfur has a larger atomic radius than oxygen; additionally, sulfur has more neutrons than oxygen.
Which of the following explains the change in atomic size that occurs as you read the periodic table from left to right across a period?
A. The number of electrons is decreasing.
Incorrect. For neutral elements, the number of protons increases as you move across a period; and for neutral compounds, the number of electrons equals the number of protons.
B. The valence shell is expanding.
Incorrect. Elements in the same period have the same number of valence shells.
C. The nuclear charge is increasing.
Correct! The increasing number of protons in the nucleus results in a stronger attraction of the electrons and consequently holds them more tightly to the nucleus. As a result, the atomic radius is generally smaller as you move across a period from left to right.
D. The neutrons remain the same.
Incorrect. While the number of neutrons for each element differs, they do not remain the same for elements across a period.
Which of the following best describes why the ionization energies of the elements increase from left to right across the Periodic Table of Elements?
A. The atomic size of the elements increases from left to right across the periodic table.
Incorrect. Atomic size generally decreases from left to right across the periodic table.
B. The valence electrons of each element decrease from left to right across the periodic table.
Incorrect. The valence number does not decrease from left to right across the periodic table.
C. The effective nuclear charge of each element increases from left to right across the periodic table.
Correct!
D. The atomic mass of the elements decreases from left to right across the periodic table.
Incorrect. Generally speaking, the atomic mass increases from left to right due to the increase in atomic number (protons). Additionally, this does not explain why the ionization energy increases from left to right across a period on the periodic table.