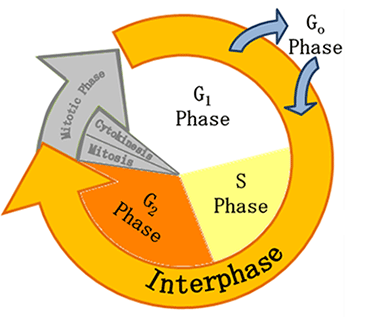
G1 - G1 stands for "Gap 1." During this phase cells carry out basic cell functions. Most cell growth occurs during G1. The cells begin to prepare for DNA replication. Proteins needed for DNA replication are made during this phase. Some cells exit the cell cycle and enter the G0 phase while other cells continue on to the S phase.
S - During the S phase, or synthesis, DNA is replicated. At the end of the S phase, one cell contains twice as much DNA as it did when it began the S phase. Cell growth continues during the S phase. It is estimated that it takes about 10 hours to replicate the information contained in the nucleus of a single human cell.
G2 - Once a cell's DNA has been replicated it will enter the G2 or "Gap 2" phase. This phase is the cell's final chance to grow. The organelles found in the cytoplasm are replicated, and more proteins are made.
G0 - G0 is referred to as the resting phase. When a cell stops dividing it enters the G0 stage. During the G0 phase, cells continue to perform all of the normal process but do not grow or divide. Some cells may never leave G0 while others skip this stage altogether. Examples of cells that enter and never leave the G0 phase are neurons (nerve cells) and red blood cells.