3x2 = 5x + 2
3x2 – 5x = 2
3x2 – 5x 3 numerator: 3x squared − 5x, denominator: 3 = 2 3 two-thirds
x2 – 5 3 five-thirds x = 2 3 two-thirds
x2 – 5 3 five-thirds x + 25 36 numerator: 25, denominator: 36 = 2 3 two-thirds + 25 36 k numerator: 25, denominator: 36
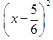 =
49
36
numerator: 49, denominator: 36
=
49
36
numerator: 49, denominator: 36
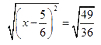
x – 5 6 five-sixths = ± 7 6 seven-sixths
x – 5 6 five-sixths = 7 6 seven-sixths or
x = 12 6 twelve-sixths
x = 2
x – 5 6 five-sixths = - 7 6 seven-sixths
x = – 2 6 two-sixths
x = - 1 3 one-third
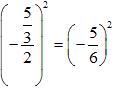 =
=
