
Conduction

Conduction

Convection

Radiation

Imagine you came in from a cold winter day. Your mother has made you a bowl of hot soup. She has placed a spoon in the bowl. When you get ready to eat the soup and grab the spoon. Ouch! The handle of the metal spoon is very hot. How did this happen? The metal spoon became hot because the spoon is in direct contact with the soup. As the heat from the soup comes in contact with the bottom of the spoon it moves up to the cooler end, all along the entire spoon up to the top. The heat moves through the spoon because the spoon is colder than the soup and because the spoon is in direct contact with the hotter soup. This type of heat transfer is known as conduction.
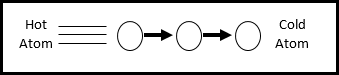
Conduction is the transfer of heat through a material by direct contact. In order for heat to move by conduction, two things with different temperatures must be touching. Conduction transfers heat by atoms colliding and transferring energy.
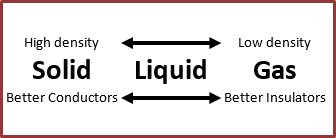
Transfer of heat by conduction usually happens in solids such as a metal spoon. In solids, the atoms are close together so there is more opportunity for the atoms to collide. Therefore, solids tend to transfer heat better than liquids or gases. Conductors increase heat transfer. Most metals are good conductors while gases tend to make good insulators.

In science class, your teacher uses a hot plate to boil some water in a beaker. As you watch the water boil you wonder how the heat moves through the water and makes all the water boil. You notice that the water keeps sinking and rising in a circular pattern.

Your teacher explains that the water at the bottom of the pot that is directly above the heat source gets hot and rises to the top of the water. It then spreads out, cools, sinks, and is heated again in a continuous cycle. This continuous cycle of hot water rising, cooling, and sinking is known as convection currents. Convection is the transfer of heat in a fluid (gas or liquid) as a result of the movement of the fluid itself.
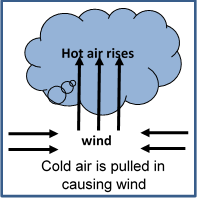
Much of the weather on earth comes from convection currents. The sun warms air at the surface of the earth. Warm air rises, causing winds. When the air cools it falls back to the ground. Without heat transfers by convection, there would be no wind, ocean currents, or mountains!

If you have ever held your hand near a candle flame, it would feel warm without your hands actually touching the flame. This also happens if you hold your hand over a hot stove. The sun can do this too. The hot stove, the sun, and fire are heat sources and can warm you even when you are not physically touching them. The type of heat transfer you are experiencing is heat transfer by radiation .

Radiation is the transfer of heat via electromagnetic waves through space. There are no solids (like giant metal spoons) touching the Sun and planet Earth and there are no fluids (substances that flow like air or water) setting up convection currents to transfer heat. Radiation transfers heat in all directions.
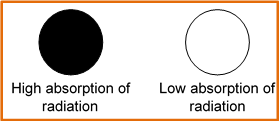
Dark colored objects absorb more radiation than light colored objects and dull objects absorb more radiation than shiny objects.