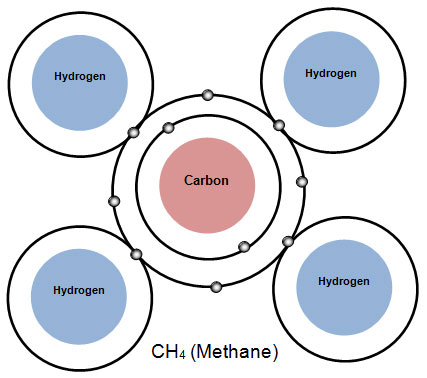
Methane is the simplest organic molecule and is the main component of natural gas.
Methane is made up of a carbon atom bonded to four hydrogen atoms.

The chemical formula for methane is CH4. Notice that in the formula CH4 there is a number written lower and smaller after the symbol for hydrogen. This is called a subscript. Subscripts show how many atoms of each element are in a compound. Since there are four hydrogen atoms in the molecule, the subscript 4 follows the symbol for hydrogen. If a symbol in a formula does not have a subscript, the number 1 is understood. In other words, there is only one atom of that element in this compound. So for methane, the ratio is 1 carbon atom to 4 hydrogen atoms.
Another way to model carbon is to use the symbols to draw what is called a skeletal structure of the compound. Below is the skeletal structure of methane.
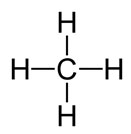
Source: Skeletal Structure of Methane, Wikimedia Commons
Using the skeletal structure to represent atoms that do not show the 3-dimensional arrangement of the atoms. Molecular model kits can be used to show the 3-dimensional structure of compounds. Models made with molecular model kits are often referred to as ball and stick models. A ball and stick model of methane is shown below.
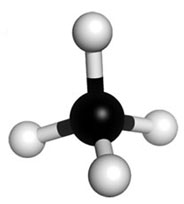
Source: Adapted From Representations of Methane, Gonzaga University
Notice that the carbon (C) has been replaced with a black ball, and the four hydrogen atoms (H) have been replaced with white balls.
![]() Now, you try building a ball and stick model of ethane. Ethane is an organic compound that is a colorless, odorless gas and is a main component of petroleum and natural gas. The formula for ethane is C2H6, and the skeletal structure is as follows:
Now, you try building a ball and stick model of ethane. Ethane is an organic compound that is a colorless, odorless gas and is a main component of petroleum and natural gas. The formula for ethane is C2H6, and the skeletal structure is as follows:
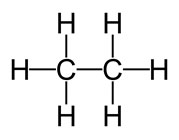
Source: Ethane skeletal structure, Wikimedia Commons
![]() Next, build a ball and stick model of butane. Butane is an organic compound that is a colorless, odorless gas and is a main component of petroleum and is used as a fuel. The formula for ethane is C4H10 and the skeletal structure is as follows:
Next, build a ball and stick model of butane. Butane is an organic compound that is a colorless, odorless gas and is a main component of petroleum and is used as a fuel. The formula for ethane is C4H10 and the skeletal structure is as follows:

Source: Butane skeletal structure, Wikimedia Commons
Fatty acids make up part of a lipid. They are long chains of carbons and hydrogen with oxygen atoms attached at one end. The flat structure of a fatty acid is shown below.
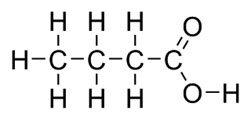
The double line between the carbon and the oxygen represents a double bond.
![]() Build the ball and stick model of this fatty acid.
Build the ball and stick model of this fatty acid.
The formula for glucose is C6H12O6, and the skeletal structure is as follows:

![]() Glucose makes a six-sided structure. Fill in the missing atoms in the ball and stick model of glucose.
Glucose makes a six-sided structure. Fill in the missing atoms in the ball and stick model of glucose.